Common Concerns About Urine Color and Odor
Urinating is a very common behavior in daily life, but once it happens frequently, it seems to be naturally associated with “kidney deficiency”:
- The smell is too strong. Is it because of kidney problems?
- The color is too dark. Does it mean my kidneys are not in good condition?
- I urinate after drinking water. Does this mean my kidneys are not in good condition?
However, are these speculations really true? How many times a day is normal for a normal person to urinate?
Urinating Frequently After Drinking Water: A Sign of Kidney Problems?
The time it takes to produce urine varies greatly from person to person, with the shortest taking only 6 to 8 minutes and the longest taking about 120 minutes. As long as the time it takes to urinate after drinking water is within this range, it is normal. Generally, a normal person’s daily urine output is about 1.5L, and the number of urination times is about 5 to 8 times a day.
Many people think that increased urination frequency is caused by kidney deficiency. In fact, most cases of frequent urination have nothing to do with kidney deficiency. Only when protein is detected in the urine can there be a problem with the kidneys.
There are many reasons for the increased frequency of urination. For example, some people have a small bladder capacity, and a little urine produced after drinking water will stimulate the bladder to produce a urination signal; some people have poor sphincter function, and the bladder storage capacity is relatively poor, and cannot store more urine.
For some people, the frequency of urination increases due to stress and emotional factors. Being in a state of high mental tension will increase the burden and pressure on the kidneys, which will promote an increase in the frequency of urination.
In addition, people with high blood sugar levels have metabolic disorders and poor ability to absorb glucose, which in turn leads to increased sugar in the urine. Even if the amount of water consumed is not large, they will go to the toilet frequently.
It should be noted that an abnormal increase in the frequency of urination may also be caused by urinary system diseases such as urethritis, urethral stones, and bladder stones. These diseases are often accompanied by symptoms such as urination pain and low back pain. It is recommended to go to the hospital for relevant examinations in time to determine the cause.
Simply put, it is normal to feel the urge to urinate soon after drinking water or to feel the urge to urinate several hours later. It is unscientific to judge the health of your kidneys based on this.

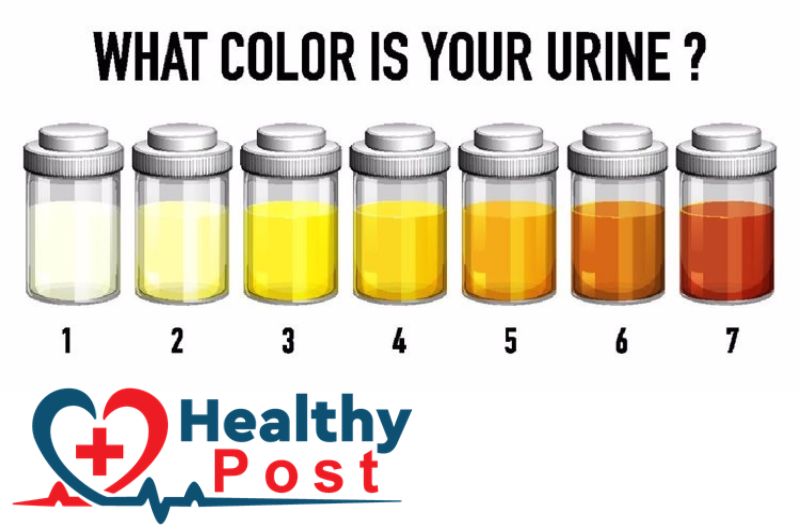
Is Yellow Urine with a Strong Odor a Warning from the Body?
The color of urine should be light yellow, but it is not fixed. It will change with the amount of water you drink. When you drink less water, the color of urine will be darker, and when you drink more water, it will be lighter. As for the smell of urine, normal fresh urine will have a light ammonia smell and no obvious odor.
Urine is a byproduct of the body’s metabolism and can also serve as a barometer of health. If you find that your urine is abnormally yellow and has a distinct odor, you must be alert to possible signals from your body. The following factors can cause urine to be abnormally yellow and have an odor:
Getting Angry
Eating a lot of spicy and irritating food, staying up late, and being in a bad mood may all cause the body to get inflamed, which can cause abnormal urination, manifested as abnormally yellow urine and a stronger odor.
Drinking Too Little Water
If you don’t drink enough water, your urine will become concentrated, darker in color, and more likely to have an unpleasant odor.
Drug Abuse
There is also a certain relationship between the color of urine and the medications taken. For example, taking drugs such as vitamin B, rifampicin, and rhubarb can also cause abnormally yellow urine. This situation can be alleviated after stopping the medication.
Food Influence
People who often eat foods rich in natural pigments such as carrots and beetroots are also prone to yellow urine, which can be relieved by reducing their consumption.
Disease Issues
Disease may also cause the urine to become abnormally darker. For example, kidney disease can cause water and sodium retention in the body, causing the urine to become concentrated and its color and odor to change.

Who is Healthier: People with Nocturia or Those Without Nocturia?
Young people should get up 0-1 times at night, and the frequency for the elderly can be relaxed appropriately, and it is normal to keep it at 0-2 times. Of course, if you occasionally have more nocturia, you don’t need to worry too much. The number of nocturia will be affected by factors such as water intake and diet.
In addition to physiological factors, the increase in the number of nocturia may also be related to disease factors. In particular, when accompanied by symptoms such as urgency, pain during urination, and abnormal urine color, it is likely to be related to prostate hyperplasia, kidney disease, urinary system disease, and abnormal heart function.
Frequent waking up at night in the elderly may cause a series of harm to their health.
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Frequent waking up at night can easily lead to orthostatic hypotension and increase the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular accidents.
Affects Sleep Quality
Frequent waking up at night will interrupt normal sleep, which will affect the next day’s mental state and work efficiency.
Increased Risk of Falls and Fractures
Data show that the risk of falling in the elderly will increase by 41% if they urinate once at night; urinating ≥3 times at night will more than double the risk of falling.
Increased Incidence of Depression
A Japanese study pointed out that patients with nocturia have a significantly increased risk of depression, and the incidence rate increases with the number of times they get up at night.
Conclusion: Monitor Your Urinary Health
Everyone should pay attention to their urine on a daily basis. If any abnormality is found, go to the hospital for relevant examinations in time, and carry out targeted treatment after identifying the cause.


