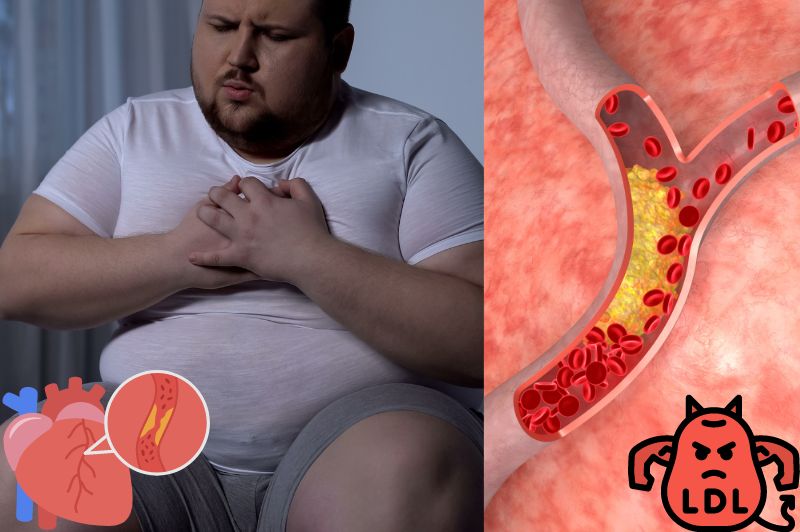
Heart disease has always been one of the health problems around the world, with a high mortality rate. Although many factors can lead to heart disease, hyperlipidemia is considered to be one of the main risk factors. This article will explore in depth how high cholesterol harms your heart and how to manage and prevent heart problems caused by hyperlipidemia through scientific methods.
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a lipid molecule that plays an important role in the human body. Cholesterol can be divided into two main types: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). LDL-C is often called “bad cholesterol” because when its levels are too high, it accumulates in blood vessels and promotes the onset of arteriosclerosis. In contrast, HDL-C is called “good cholesterol” because it helps remove excess cholesterol from blood vessels.
The Link Between High Cholesterol and Heart Disease
The link between high cholesterol levels and heart disease has been extensively studied and established. A large body of scientific evidence shows that high LDL-C levels are strongly associated with the risk of coronary heart disease. When LDL-C levels are elevated, it can lead to the formation of cholesterol plaques within the arteries, which gradually grow and eventually restrict the ability of blood to flow to the heart. This condition is called atherosclerosis and is one of the main causes of heart disease.
In addition, this condition is closely related to the risk of heart attack. When cholesterol plaques in the arteries rupture, they can cause blood clots to form, blocking the blood flow to the heart, leading to a heart attack. This condition can lead to serious consequences, including myocardial infarction.
Causes of High Cholesterol
Understanding the causes of high cholesterol is important for preventing and managing heart problems. Here are some of the main causes of high LDL-C levels:
Dietary Habits
Eating high-fat, high-cholesterol foods is one of the main causes of high LDL-C. Cholesterol and saturated fat in food can increase the LDL-C level in the blood.
Genetic Factors
Family heredity can also affect an individual’s cholesterol levels. If there is a history of heart disease or high cholesterol in your family, you may be at a higher risk.
Lack of Exercise
Lack of physical activity and exercise can lead to weight gain, which in turn affects cholesterol levels. An active lifestyle can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
Smoking
Smoking damages the lining of your blood vessels, making them more susceptible to damage, thereby increasing the risk of cholesterol plaque formation.
Age and Gender
Cholesterol levels tend to rise as we age, usually starting after age 40 for men and 50 for women.
The Dangers of High Cholesterol
The harm that high cholesterol can do to your heart cannot be underestimated. Here are some of the health problems that high LDL-C levels may cause:
Coronary Heart Disease
High cholesterol is one of the main risk factors for coronary heart disease. Coronary heart disease refers to a disease in which the blood supply to the coronary arteries is insufficient, leading to ischemia of the heart, which can cause myocardial infarction in severe cases.
Myocardial Infarction
When a cholesterol plaque ruptures and forms a blood clot, it may completely block a coronary artery, causing a myocardial infarction, a serious heart event that can be fatal.
Stroke
High cholesterol is also associated with an increased risk of stroke because blood clots can affect blood supply to the brain, leading to a stroke.
Peripheral Arterial Disease
High cholesterol levels can also affect blood vessels in other parts of the body, such as the arteries in the legs, leading to peripheral arterial disease, which can lead to limb ischemia and gangrene.
How to Detect and Diagnose Cholesterol Issues
To find out an individual’s cholesterol levels, doctors usually do a blood test. This test usually includes measuring the levels of total cholesterol, LDL-C, and HDL-C. With this data, doctors can assess a person’s risk of heart disease.
Based on your cholesterol level and other risk factors, your doctor can make a diagnosis and recommendations. If high cholesterol is found, your doctor may recommend changing your diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, or taking medications to reduce your risk of heart disease.
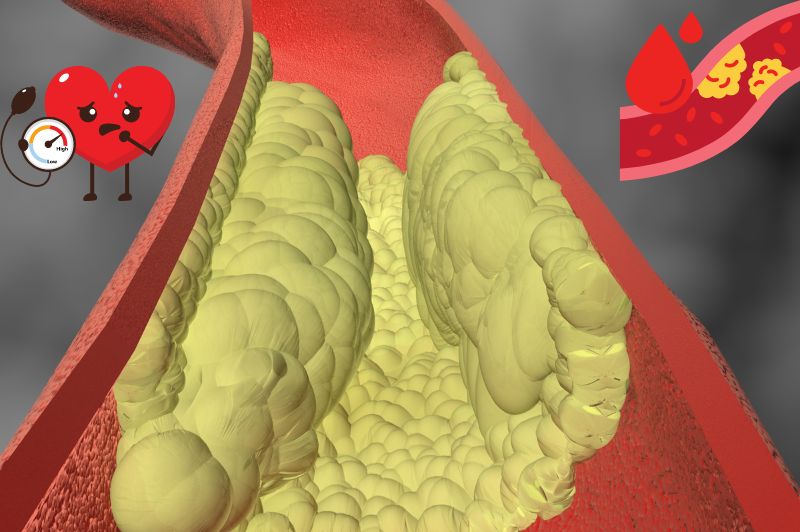
Ways to Manage High Cholesterol
Managing high cholesterol levels is an important step in preventing heart disease. Here are some ways to lower your LDL-C levels:
Healthy Eating Habits
- Control Saturated Fat Intake: Reduce the consumption of high-saturated fat foods such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, butter, etc., as they will increase LDL-C levels.
- Increase Unsaturated Fats: Choose healthy fat sources, such as olive oil, nuts, fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids), etc., which can help increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels while lowering LDL-C levels.
- Eat More Dietary Fiber: Dietary fiber can help lower LDL-C levels. Increase the intake of vegetables, fruits, whole-grain products and beans.
- Control Cholesterol Intake: Avoid eating high-cholesterol foods such as egg yolks, animal offal, etc.
Moderate Exercise
- Perform Aerobic Exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, etc., can significantly increase HDL-C levels and help remove excess cholesterol.
- Increase Muscle Mass: Strength training helps increase your basal metabolic rate, helping to control your weight and cholesterol levels.
Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking is one of the key steps in preventing heart disease. Smoking damages the lining of your blood vessels and increases the risk of cholesterol plaque formation.
Control Your Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight helps control cholesterol levels, as obesity is associated with high LDL-C levels. A balanced diet and adequate exercise are key to maintaining a healthy weight.
Limit Alcohol Intake
Alcohol intake should be kept in moderation, as excessive drinking will increase LDL-C levels.
Drug Treatment
In some cases, diet and lifestyle changes may not be effective in lowering LDL-C levels. Your doctor may consider prescribing medications, such as statins, to help lower cholesterol levels. Medication is usually considered when lifestyle interventions such as diet and exercise are ineffective or when there is a high risk of developing the disease.
Regular Testing
Regular cholesterol level testing is key to monitoring and management, especially for those with a family history of risk or other risk factors for heart disease. Based on the test results, the doctor can develop an appropriate treatment plan based on the individual’s condition.
Take Control of Your Heart Health Today!
Don’t wait to address high cholesterol and its risks. Schedule a cholesterol screening with your healthcare provider to understand your levels and take proactive steps toward managing them. Embrace a heart-healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and routine check-ups. Your heart health is in your hands—act now to protect it and enjoy a longer, healthier life!
Conclusion
High cholesterol is a significant risk factor for heart disease, but through a healthy lifestyle and timely medical intervention, we can reduce the risk of heart disease. Always pay attention to your cholesterol level and take appropriate measures according to your doctor’s advice to manage and prevent heart problems caused by high cholesterol. Through scientific methods, we can better protect our heart health and enjoy a longer life.