Heart attack is a serious medical emergency. If you don’t recognize it and do not take action in time, it may lead to serious consequences or even be life-threatening. Therefore, it is crucial for everyone to know the signs of a heart attack. This article will introduce the common signs of a heart attack and the countermeasures in detail to help everyone make the right judgment and take correct actions when faced with this situation.
Common Signs of a Heart Attack
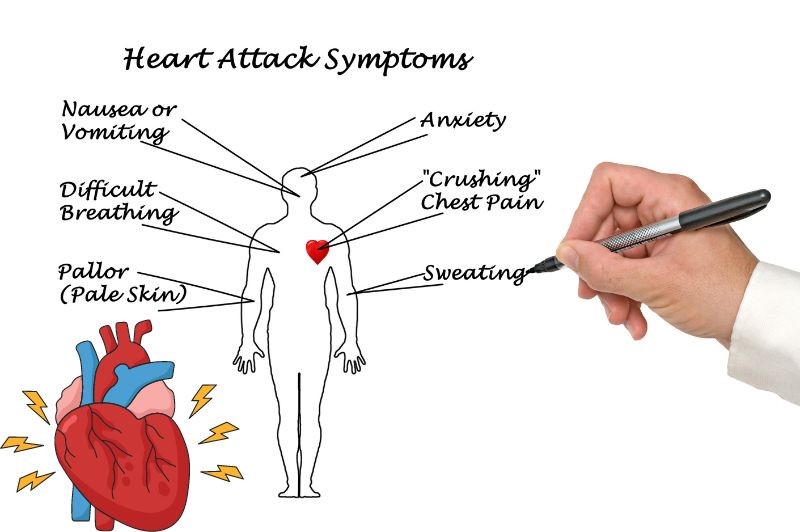
Signs of a heart attack vary from person to person, but they usually include the following:
Chest Pain
Chest pain is one of the most common symptoms of a heart attack. This pain is usually located behind the sternum and may radiate to the left arm, neck, jaw, or back. The pain may be a sense of pressure, tightness, or burning, and may last from a few minutes to a few hours.
Dyspnea
During a heart attack, the patient may experience shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, especially when moving or lying down.
Nausea and Vomiting
Some patients may experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting during a heart attack.
Sweating
Sudden and heavy sweating, especially when accompanied by symptoms such as chest pain, should alert you to the possibility of a heart attack.
Fatigue and Weakness
Before a heart attack, patients may feel abnormally fatigued and weak, and even unable to complete daily activities.
In addition to the common symptoms above, some heart attack patients may also experience atypical symptoms such as syncope, palpitations, anxiety, etc. Therefore, when any physical symptoms that are different from usual occur, they should be taken seriously.
Things to Note When Recognizing a Heart Attack
Here are some things to look for when recognizing the signs of a heart attack:
Duration and Severity of Symptoms
Symptoms of a heart attack usually last from a few minutes to a few hours and are more severe. If the symptoms are short-lived and mild, it may not be a heart attack; but if the symptoms continue to worsen or cannot be relieved, seek medical attention immediately.
Accompanying Conditions
Symptoms of a heart attack may be accompanied by other signs, such as arrhythmia, decreased blood pressure, etc. While observing the symptoms, also pay attention to other changes in the body.
Personal Medical History and Risk Factors
People with a history of chronic diseases such as high blood pressure, high blood lipids, diabetes, and those with higher risk factors for heart disease such as smoking and obesity should be more alert to the possibility of a heart attack.
Measures to Deal with a Heart Attack
After recognizing the signs of a heart attack, you should take the following immediate steps:
Call the Emergency Number
Call the local emergency number as soon as possible, inform the patient’s condition and address, and wait for the arrival of professional medical personnel. While waiting, try to stay calm and don’t panic.
Keep Quiet and Rest
When a heart attack occurs, the patient should try to keep quiet and avoid hard exercise or emotional excitement. You can lie down or sit down to rest and maintain a comfortable position.
Take Emergency Medication
If the patient has emergency medication for heart disease prescribed by a doctor (such as nitroglycerin), he or she can take it according to the doctor’s instructions if the symptoms meet the medication requirements. However, do not abuse or misuse the medication.
Inform Family or Friends
When responding to a heart attack, inform family or friends of the patient’s condition and location so that they can assist in responding or provide necessary support.
Measures to Prevent Heart Attacks
In addition to knowing the signs of a heart attack and what to do if you are having one, it is equally important to prevent one. Here are some things you can do to prevent a heart attack:
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle including a proper diet, moderate exercise, smoking cessation and alcohol restriction, and adequate sleep can help reduce the risk of heart attack.
Control Chronic Diseases and Risk Factors
Patients with chronic diseases such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes should actively treat and control their conditions; at the same time, pay attention to reducing risk factors for heart disease, such as losing weight and improving psychological stress.
Regular Physical Examinations and Consultations
Have regular physical examinations to understand your physical condition and heart disease risk; if you have any concerns or symptoms, consult a professional doctor in a timely manner and receive appropriate examinations and treatments.
Conclusion
A heart attack is a serious medical emergency that requires prompt recognition and response. By understanding the common signs and precautions of a heart attack, we can make the right judgment and take the right action at the critical moment. At the same time, preventing heart attacks is equally important. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and controlling chronic diseases and risk factors, the risk of heart attacks can be reduced.


